No products
Prices are tax included
Product successfully added to your shopping cart
There are 0 items in your cart. There is 1 item in your cart.
CCTV Information

WHAT IS VIDEO SURVEILLANCE?
Video surveillance is a rapidly growing field. However, understanding the technical terminology used in this area can be challenging. The purpose of this page is to help you better comprehend video surveillance by explaining the main terms and concepts associated with it (it's important to note that surveillance cameras are not strictly dedicated to "security". They are more commonly used for doubt resolution and visual monitoring).
KEY TERMS
Surveillance cameras are the central component of a video surveillance system. It captures images and videos of the monitored environment. Here are some terms commonly used to describe the features of cameras:
Sensor: The camera's sensor converts light into electrical signals. It is metaphorically the "eye" of the device.
Frames Per Second (FPS): Frames Per Second (FPS) is an essential consideration for security cameras. FPS indicates the quantity of individual frames or images that a camera records in a single second.

In scenes with rapid movement, such as a fast motorway or a casino's roulette wheel, a higher frame rate is crucial for clear imagery. However, this comes with increased demands for storage, processing power, and energy. Alternatively, settings with slower activity, like a reception area or an office, can be effectively monitored using a lower frame rate, which is more economical.
For forensic purposes, particularly when the main aim is to identify individuals in areas like entryways, a combination of a lower frame rate and higher resolution is often favoured. This method efficiently captures detailed facial features for identification, striking a balance between resource utilisation and image quality.
Resolution: This refers to the number of pixels the camera's sensor can capture. A higher resolution provides a more detailed image.
FHD / 2K / 4K: These are common display resolutions used to describe the video quality of a surveillance camera. FHD (Full HD) corresponds to a resolution of 1920×1080 pixels, 2K to a resolution of 2560×1440 pixels, and 4K to a resolution of 3840×2160 pixels. A higher resolution offers a sharper and more detailed image but may also require more storage space.

Megapixels (MP): Megapixels are a crucial measure of a surveillance camera's resolution. Each megapixel equals one million pixels, thus determining the sharpness and detail of an image. A camera with more megapixels captures sharper, more detailed images, allowing for effective zooming while maintaining image clarity. However, higher resolutions result in larger file sizes and increased storage and bandwidth requirements. It's common to see the megapixel count associated with the corresponding resolution designation "FHD / 2K / 4K".
Lens (Optical Zoom / Digital Zoom): The lens determines the camera's field of view and focal length. There are fixed lenses and adjustable (motorized) lenses. The lens enables the device to zoom, either through mechanical action, known as "optical zoom," or via software, referred to as "digital zoom."
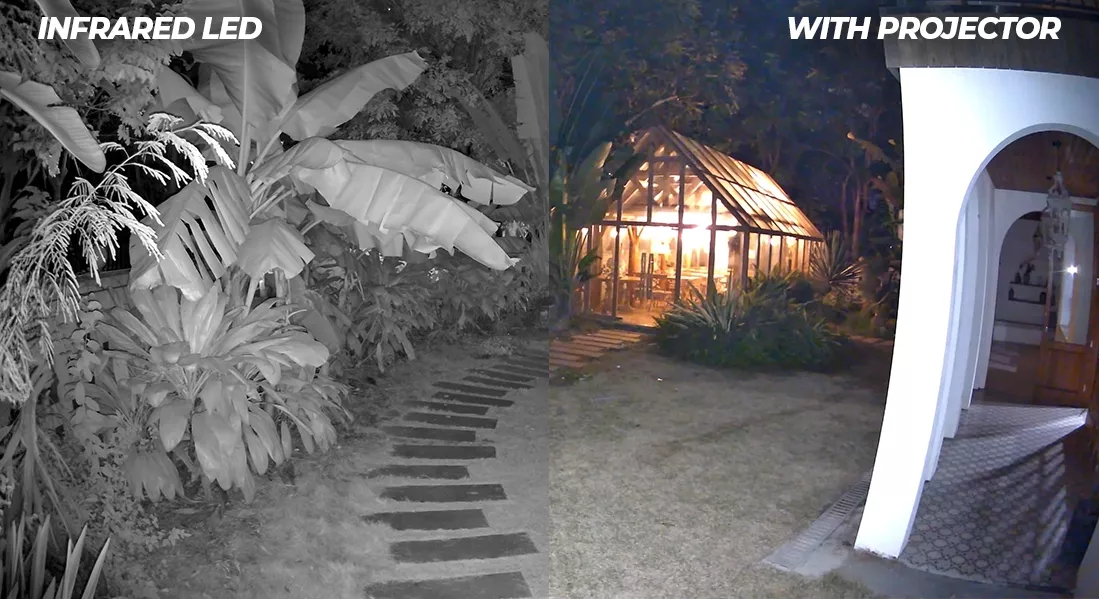
Night Vision: Night vision in cameras is a crucial aspect of continuous surveillance. Cameras equipped with infrared LEDs provide night vision by emitting invisible infrared beams. This allows for clear visualization of objects and movements in total darkness discreetly.
(Note: If the IR is too powerful, this may result in an image too bright to distinguish a facial identification / license plate - installation height /distance is crucial for facial / license plate identification with IR. Always refer to the manual for recommended installation height.)
For color night vision, it's necessary to choose a camera equipped with one or more LED projectors. These projectors illuminate the scene with visible light, enabling night surveillance with colored details, which can be useful in scenarios where color is important for identifying and distinguishing objects and individuals.

Intelligent Detection: This feature enables compatible video surveillance cameras to analyze captured images in real-time and automatically detect specific events or behaviors. This image analysis is based on motion recognition algorithms powered by artificial intelligence. The device can distinguish between humans, vehicles, and animals (specific to the camera). This technology enhances surveillance efficiency by generating alerts in case of abnormal activity, allowing for rapid response to potential incidents and facilitating data management by eliminating unnecessary recordings.
Note: This functionality depends on the camera's hardware-software compatibility.
Intelligent Tracking: A camera with a motorized sensor unit can pivot horizontally and/or vertically, providing a critical advantage in video surveillance. Thanks to its integrated software, it can continuously track and record movements of individuals, vehicles, or even animals once detected. This feature significantly enhances the efficiency of the surveillance system, ensuring dynamic and responsive coverage for increased security and correct notification.
Timelapse: Compatible with certain surveillance cameras, this feature allows the capturing and condensing of long time periods into a short, speeded-up video. It's useful for observing gradual changes such as sunrise and sunset, plant growth, the construction/renovation of a structure, or the movement of traffic. By creating a fast-forwarded visual representation, this function offers a unique perspective on the evolution of events over an extended period in a shortened timeframe.
Note: For this to work, the camera takes a series of photos at regular intervals. You set this interval from the available options: the number of shots taken determines the length of the video and the size of the exported file.

Wide-Angle / FOV: The wide-angle (FOV, or Field of View) feature in surveillance cameras provides an expansive, panoramic view of the monitored environment. Measured in degrees, the viewing angle can be calculated horizontally, vertically, and/or diagonally. This data is often referred to as "Field of View" or "FOV." A wide-angle sensor captures a broader field of vision, thereby reducing blind spots and providing more comprehensive coverage. This characteristic is particularly beneficial for monitoring large areas such as lobbies, carparks, or warehouses, allowing for effective surveillance with fewer cameras and offering a better overall perspective of activities in the monitored area.
IP / IK Certification: IP certification is an international standard used to assess the degree of protection a camera offers against solid particles and liquids. "IP" stands for "Ingress Protection," followed by two numbers. The first number indicates protection against solids (dust) on a scale from 1 to 6, and the second number indicates protection against liquids (water) on a scale from 1 to 8.
Note: The higher the numbers, the greater the degree of protection. For example, an IP68 certification ensures strong resistance to dust and prolonged immersion in water.
IK certification, also known as the impact resistance rating, assesses a camera's ability to withstand physical impacts. The IK rating is followed by a number indicating the level of shock resistance, ranging from IK00 (no protection) to IK10 (maximum protection). This classification helps in choosing cameras capable of withstanding environmental rigors and maintaining their functionality despite potential physical shocks.
( Note: IK cameras are coming to Ultra Secure soon)
POWER SUPPLY TYPES
Cameras require an electrical power source to operate. This can be provided by power adapters, PoE (Power over Ethernet) supplies for compatible cameras. It's now possible to have completely stand alone cameras, which can operate on battery power and be charged via solar panels.
DC5V / DC12V: These are power supply options for video surveillance cameras. DC5V indicates a 5-volt power supply, while DC12V indicates a 12-volt power supply. These specifications denote the type of power source required to operate the camera and can vary depending on the model and the device's requirements.
Autonomous / Battery-Powered: Without compromising recording quality or smart features, some cameras can operate completely autonomously. The batteries need to be periodically recharged using the provided power cable (or via a compatible solar panel).

PoE: PoE (Power over Ethernet) is a feature that enables a video surveillance camera to be powered and transmit data using a single Ethernet cable! This eliminates the need for an external power source, and separate data cable for the camera, simplifying installation and reducing the number of cables required.
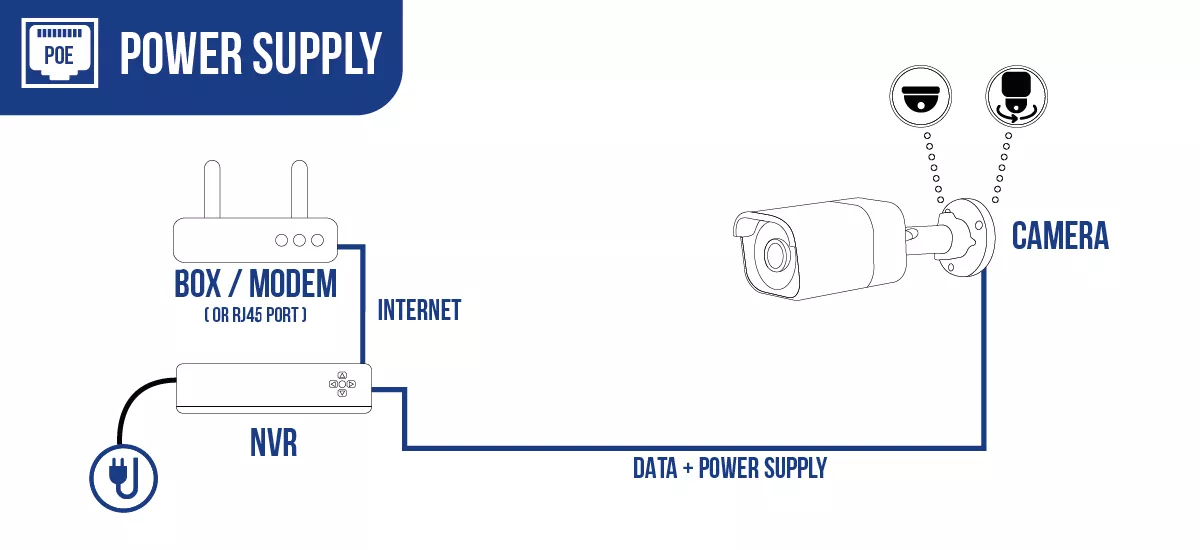
DIFFERENT CONNECTIONS
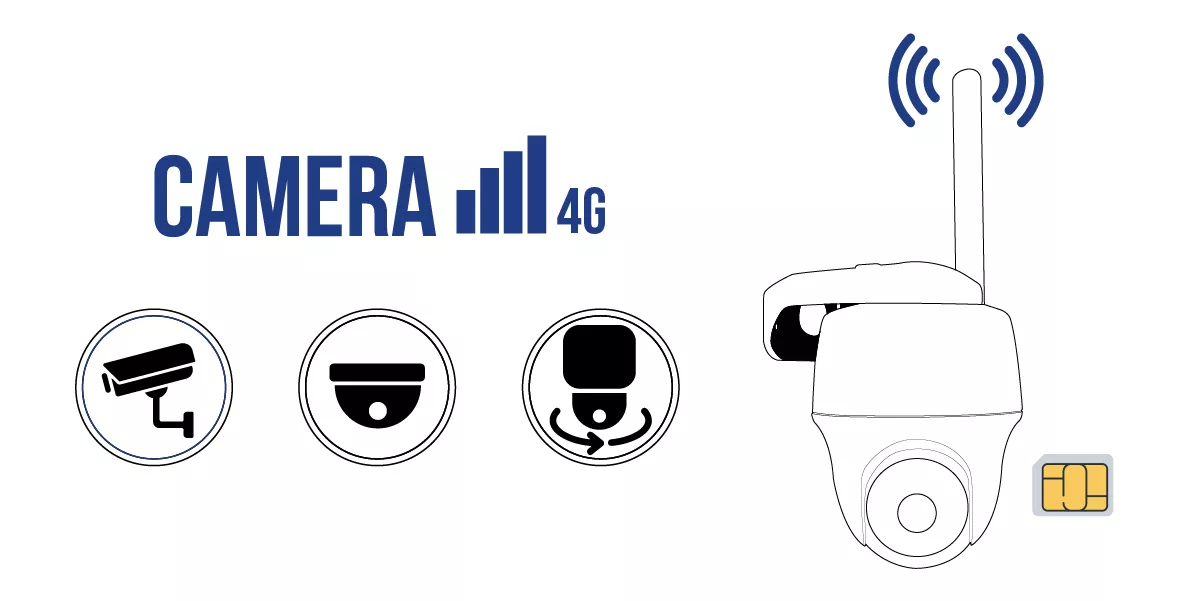
Surveillance cameras can connect to a home network (wired or wireless), but if you wish to install them in a more isolated area, they can also be equipped as "GSM" or "4G LTE" cameras.
WiFi: The WiFi connectivity of cameras offers cable-free placement flexibility, enabling easy remote access. Cameras operating on 2.4 GHz provide a broader range, but may be prone to interference. Those supporting both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz benefit from faster speeds and better resistance to interference, ideal for high-quality videos and more reliable connections in crowded environments. The choice between these options depends on the desired range and specific usage conditions.
4G/GSM: Surveillance cameras equipped with 4G/GSM connectivity can connect to a cellular network to transmit captured videos and images. In this scenario, the camera must be equipped with a SIM card activated by a carrier. This enables monitoring of locations where there is no wired internet access or in cases of lost wired connectivity.
ULTRACAM, ALL-IN-ONE VIDEO SURVEILLANCE!
Ultra Secure have developed the simplest and most effective surveillance system: UltraCAM. Free from constraints in setup, installation, and usage (eliminating the need for complex cable, network, or camera power management), it's ideal for quickly and durably equipping your home, apartment, holiday home, business, construction sites and buildings in progress.
DIFFERENT TYPES OF STORAGE (INTERNAL MEMORY, SD, NVR...)
Internal Memory: Internal memory refers to the built-in storage capacity of the camera itself. This can vary depending on the model, offering limited space for storing recordings.
(Note: Don't worry about the camera running out of storage space; it's programmed so that the most recent recordings overwrite the oldest ones.)
Micro-SD Card: These are removable memory cards that offer flexible and expandable storage capacity. Cameras equipped with micro-SD card slots allow users to insert a card of a chosen capacity (up to the camera's maximum supported limit) for recording and storing videos. This makes backing up and transferring recordings to other devices convenient.
(Note: Video transfers can also be done directly via the free application provided with the camera.)
NVR: The Digital Video Recorder (NVR) is the device responsible for recording and storing videos from surveillance cameras. Here are some terms associated with these devices:
Number of Channels: The number of channels indicates how many cameras can be connected to the recorder for simultaneous recording of one or more streams.
(Note: Remember, if a camera has multiple lenses, the number of channels occupied is equivalent to the number of lenses on the camera.)
Video Compression: Video compression reduces the size of video files to save storage space. Common compression formats include H.264 (AVC) and H.265.(HEVC) H264 generally uses more storage than H265 for example. H265 offers a higher compression ratio and better image quality with less video artifacts.
Storage: Video recorders can use various types of storage, such as internal or external hard drives. The storage capacity is a factor to consider based on your needs and number of cameras.


